Som et materiale med fremragende korrosionsresistens, Edelstål bruges det vidt og bredt i forskellige industrier, såsom byggeri, automobiler, luftfart, husholdningsapparater og medicinsk udstyr. I vores daglige liv kan vi nogle gange opdage, at nogle rustfrie stålvarer er magnetiske, mens andre ikke er det. Er rustfritt stål magnetisk? For at finde dette ud af skal vi forstå sammensætningen, strukturen og de magnetiske egenskaber ved rustfrit stål.
Hvad er magnetisme?
Magnetisme lyder som en superkraft i science fiction-filmer, men det er faktisk blot evnen til for et stof til at reagere på et magnetfelt. Kort sagt er magnetisme evnen til for et stof at "trække" eller "afvise" et magnet. Hvert materiale har forskellige magnetiske egenskaber, og den magnetiske situation for edelstål er meget forskellig.
Klassifikation af Edelstål :
Edelstål er en jernbaseret legeme med en bestemt mængde krom, nickel, molibdad og andre elementer, der er specielt smeltet og behandlet. På grund af dets fremragende korrosionsmodstand, gode mekaniske egenskaber og stærke oxidationsmodstand bruges det vidt omfattende i forskellige områder. Der findes mange typer edelstål, som kan inddeles i forskellige typer efter deres krystalstruktur og sammensætning.
 Martensitiskt Edelstål:
Martensitiskt Edelstål:
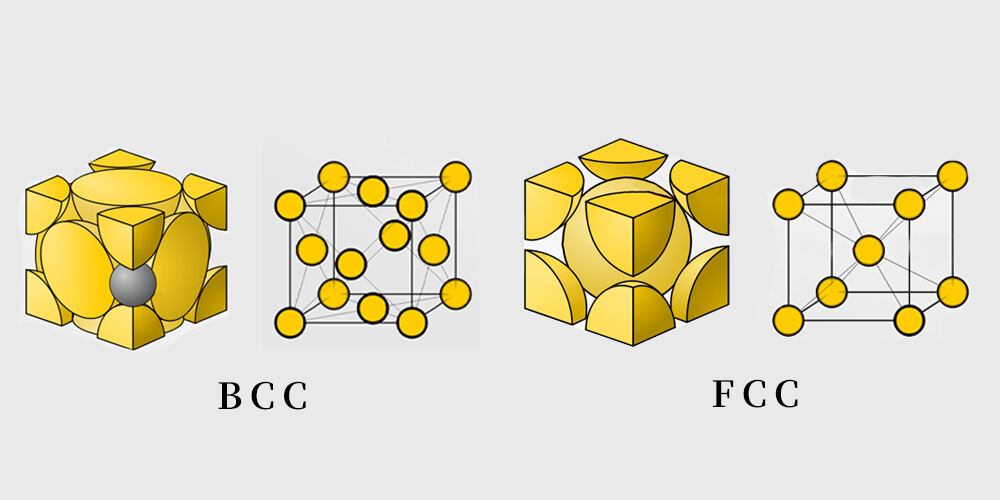
Martensitisk rostfri stål er en jernbaseret legering med høj kulge indhold, som har egenskaberne høj hårdhed, høj styrke og kraftigt magnetisme. Dets hovedkomponenter omfatter jern, chrome, kul og andre elementer. Typiske martensitiske rostfrie ståle inkluderer 410 og 420. Fordi dets krystalstruktur er en kropscentreret kubisk struktur (BCC), har det kraftigt magnetisme. Dette skyldes, at placeringen af jernatomer i BCC-strukturen tillader eksistensen af elektronspinning og magnetisk moment, hvilket genererer magnetisme.
 Austenitisk rostfrit stål:
Austenitisk rostfrit stål:
De mere almindelige austenitiske edelståltyper er 304 og 316, hvis krystalstruktur er en cubic-centered face struktur (FCC). Opstillingen af jernatomer i den cubic-centered face struktur gør magnetismen svag eller endda forsummelig. På grund af de specielle egenskaber ved denne struktur er austenitisk edelstål normalt ikke-magnetisk. Dog kan dels af austenitstrukturen under koldearbejde (som polering, slipning, trådtrækning osv.) eller høj spænding blive omformet til martensit, hvilket viser en vis grad af magnetisme.

 Ferritisk Edelstål:
Ferritisk Edelstål:
Ferritisk edelstål er en type edelstål, der indeholder mindre kul og hovedsagelig består af jern og krom. Dens krystalstruktur er en body-centered cubic struktur (BCC). Ferritisk edelstål, såsom type 430, har normalt tydelig magnetisme. Ferritisk edelstål har stærk magnetisme, hvilket hovedsagelig skyldes dens høje jernindhold.
 Duplex Edelstål:
Duplex Edelstål:
Duplex stainless steel kombinerer egenskaberne af austenit og ferrit og har normalt høj styrke og korrosionsmodstand. Dets struktur består af 50% austenit og 50% ferrit, så i forhold til magnetisme er deres ydelse mere kompleks, med både nogle magnetiske og ikke-magnetiske egenskaber fra austenitisk stainless steel.
Faktorer, der påvirker magnetydelserne af stainless steel :
Kemisk sammensætning:
Kemisk sammensætning af stainless steel påvirker direkte dets magnetisme. For eksempel vil tilføjelsen af mere nickel fremme austenitisering og gøre stainless steel ikke-magnetisk. Elementer som krom, jern og kul har en vis effekt på magnetisme, især ferritisk stainless steel med et højere indhold af krom har normalt en stærkere magnetisme.
forarbejdningsproces:
Koldbearbejdning kan forøge magnetisme ved at indføre stress og gitterforstyrrelse, hvilket forårsager at austenit transformerer til martensit. Varmehandling ændrer imod crystalstrukturen gennem varme- og køleprocesser, hvilket kan føre til svækkelse eller forstærkelse af magnetisme.
Temperaturindsats:
Under lavtemperaturbetingelser kan austenitisk edelstål delvist transformerer til martensit, hvilket resulterer i forøget magnetisme; mens under højtemperaturbetingelser er magnetismen af austenitisk edelstål normalt svækket eller endda fuldstændig tabt.
Hvordan vælger man?
Rostfri stål bruges bredt i mange områder, og magnetisme er også en af de faktorer, der skal tages i betragtning. I nogle tilfælde kan materialets magnetisme ikke ignoreres, især i miljøer, der involverer magnetiske felter eller elektromagnetisk forstyrrelse. I andre tilfælde kan ikke-magnetisk rostfrit stål være mere populært, især inden for medicinsk og fødevarebehandling, hvor enhver magnetisk forstyrrelse skal undgås. For eksempel kræver medicinske apparater og fødevarebehandlingsudstyr ofte brug af ikke-magnetisk rostfrit stål for at undgå forstyrrelse af instrumenter eller for at undgå blanding af metalpartikler i maden. Ved bilproduktion kan magnetisk ferritisk rostfrit stål bruges vidt omkring i dele som karosserier.
Er edelstål magnetisk? Svaret er ikke absolut. Om edelstål er magnetisk afhænger af dets sammensætning, struktur, bearbejdnings teknologi og eksterne vilkår. At forstå det magnetiske ydelse af forskellige typer edelstål er meget vigtigt for materialevalg og praktisk anvendelse.
Vi er en professionel stålprodusent. Hvis du har nogen behov, kan du kontakte os når som helst!
 +86 17611015797 (WhatsApp )
+86 17611015797 (WhatsApp )  info@steelgroups.com
info@steelgroups.com
